The use of the medical protective clothing
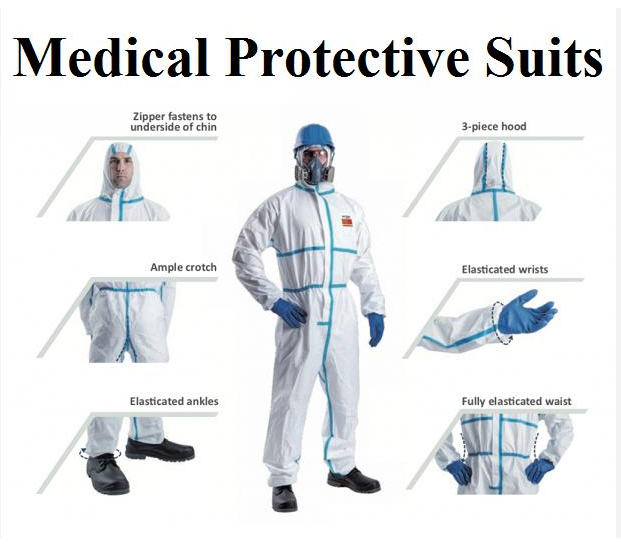
Medical protective clothing, also known as personal protective equipment (PPE), is crucial for safeguarding healthcare workers and patients from infectious diseases, blood, and bodily fluids. It acts as a barrier, reducing the chance of exposure and transmission of germs. Effective use of PPE involves proper selection, donning (putting on), doffing (taking off), and disposal, along with training on these procedures.
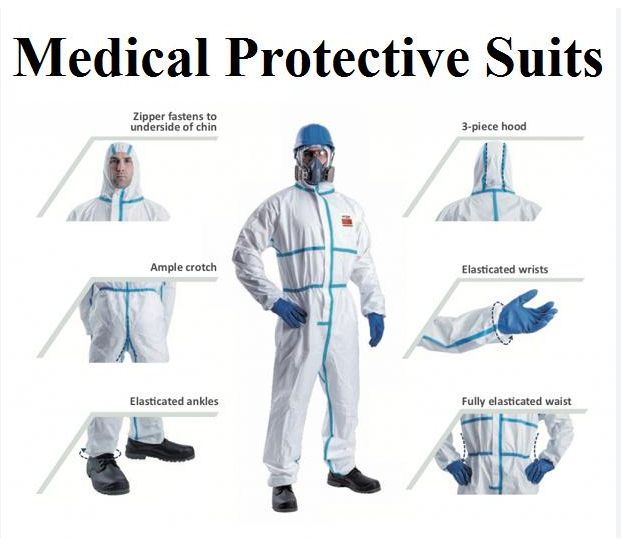
Key aspects of medical protective clothing:
Purpose:
To prevent the spread of infections and protect against hazardous substances.
Types:
Includes items like gloves, gowns, shoe covers, head covers, masks, respirators, eye protection, and face shields.
Importance of Proper Use:
Essential to minimize contamination and ensure the safety of both healthcare professionals and patients.
Levels of Protection:
PPE is categorized into different levels based on the degree of protection needed, with Level A offering the highest level of respiratory, skin, and mucous membrane protection.
Risk Assessment:
Employers are responsible for assessing workplace hazards and providing appropriate PPE along with training.
Examples in Healthcare:
PPE is commonly used in hospitals, doctor's offices, and clinical labs.
Specific examples:
Gowns: Protect skin and clothing from infectious droplets and splashes.
Gloves: Protect hands from direct contact with potentially infectious materials.
Respirators: Filter the air and protect against airborne pathogens.
Face shields: Protect the face from splashes and sprays.
Surgical masks: Protect the nose and mouth from bodily fluids.
Medical Textiles:
Medical protective clothing is often made from medical textiles, including nonwoven fabrics, which are popular for disposable items like surgical masks and gowns due to their barrier properties and ease of manufacturing.
Standard Precautions:
Standard precautions, which include the use of PPE, are required when there is a potential for contact with a patient's blood or body fluids.
Regulatory Oversight:
In some countries, PPE is regulated as a medical device, and organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) provide guidance on its safe use.
 Send Email
Send Email